“Don’t find the fault, find the remedy.” – Henry Ford
In contrast to healthcare professionals, the government, regulators, security experts, and health tech entrepreneurs aren’t seeing EMR in the same way.
Discussions about issues linked to EMRs are very common among providers.
However, since the time human brains figured out advanced yet practical use cases for blockchain technology, we very often end up catching up with those few people discussing the remedies.
We are going to do exactly the same – for the next 5 minutes.
We will connect the dots and understand how blockchain-based EMRs solve existing problems that providers can’t stop themselves from discussing.
The existing problems with EMRs, making it the most outdated healthcare innovation
EMRs are designed and built to keep very sensitive information of patients in a secure and private manner.
However, intruders and hackers can easily outsmart the current security mechanism of EMRs.
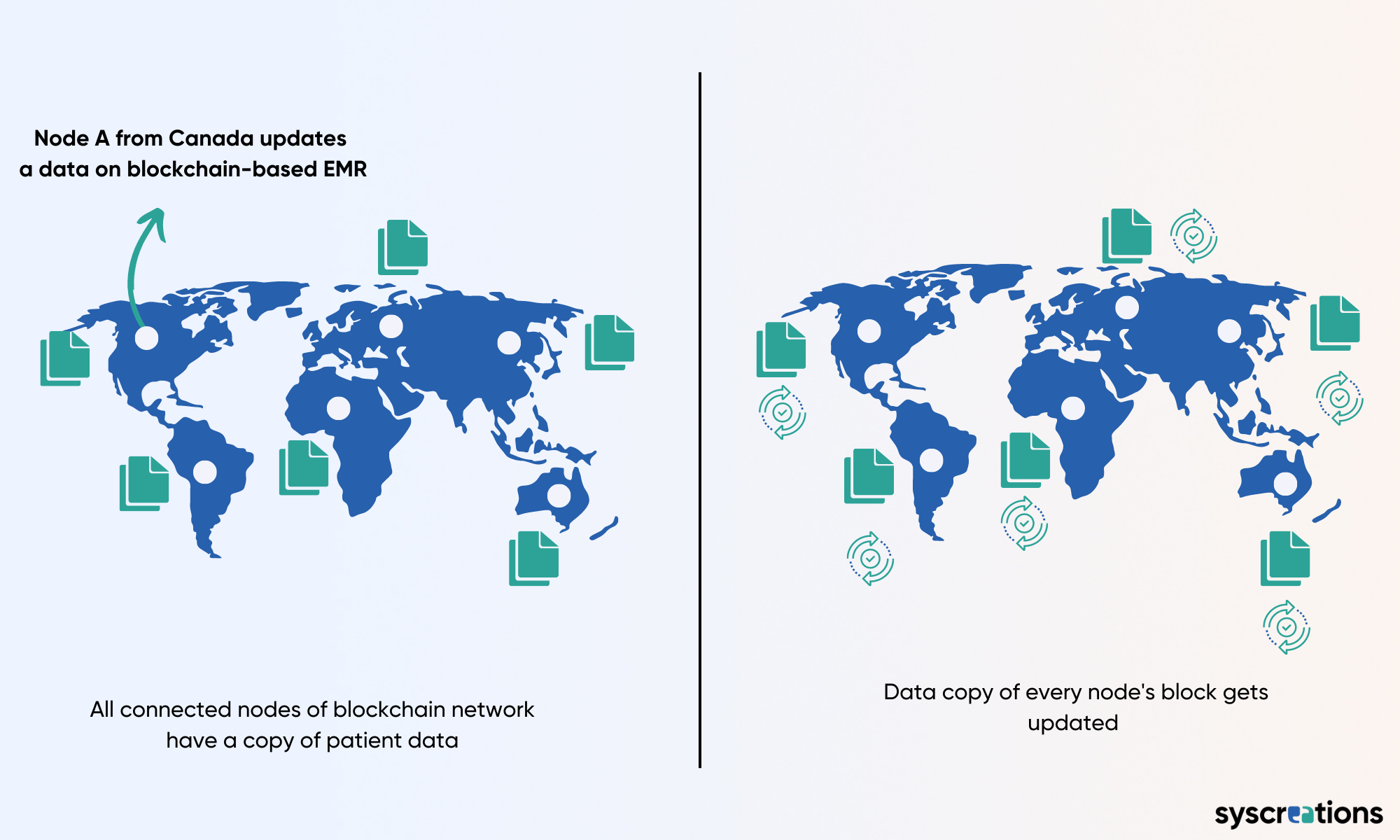
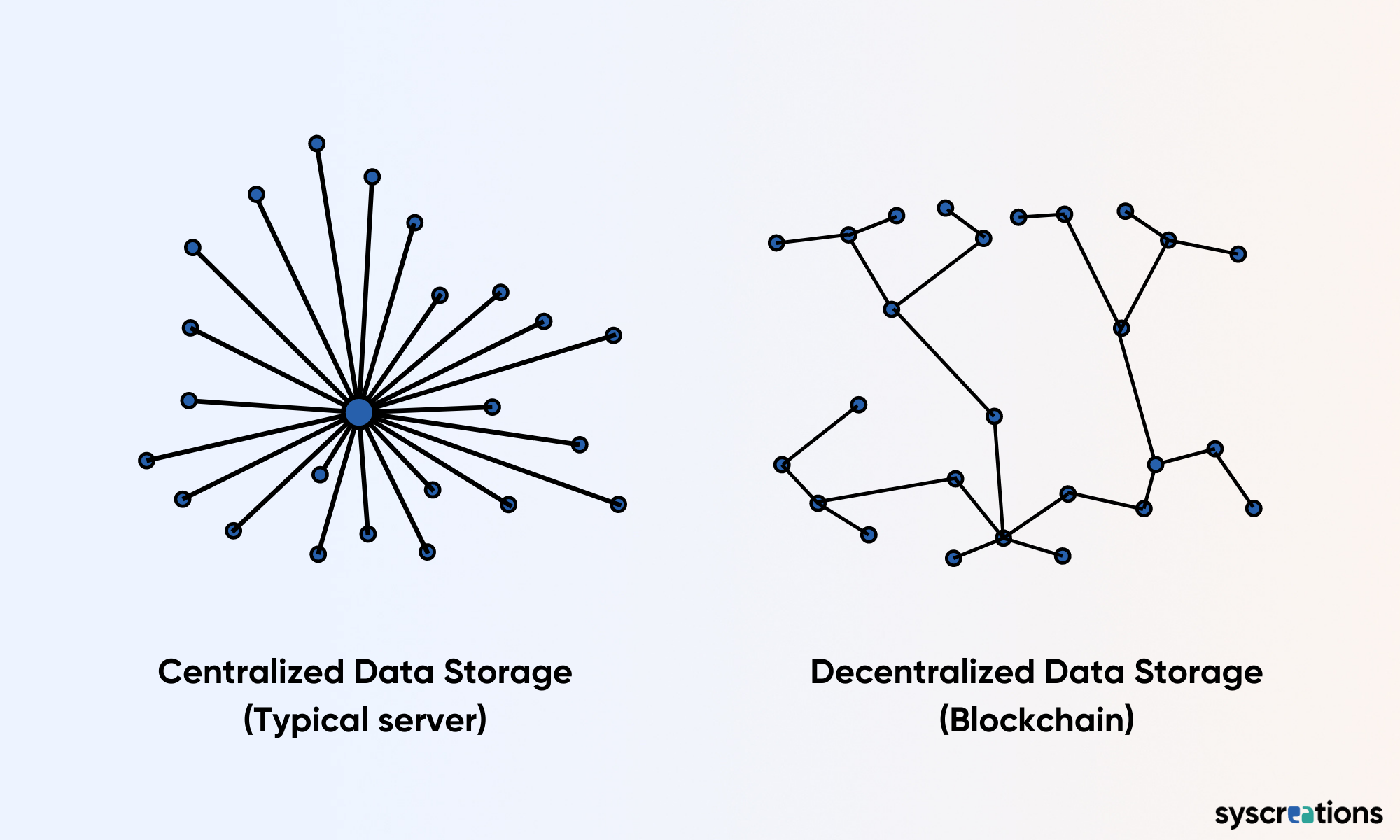
First, crucial private data of patients are stored in a very centralized way.
Access to that one server, computer or node creates a smooth path for intruders to steal all the data.
Second, it is extremely possible to – if not steal – but tamper with data and even permanently delete the data as there is a single authority controlling the EMR and data stored on it.
Third, it is impossible for patients to prove their ownership of the data and control who can access it.
Fourth, the very ‘that is not my job’ nature of EMRs enables data to be circulated within the virtual boundaries of a single organization only.
This leaves providers with no choice but to share data with someone outside of the organization via fax and email which increases the possibility of data stealing, breaching and tampering.
In essence, the problem is not with EMRs, but with the way it handles patient data.
Thus, EMRs do not require a complete makeover. The remedy is within a more advanced and robust security mechanism fueled by blockchain!
Presenting blockchain-based EMR as a remedy: The henry ford moment of healthcare is finally here
Blockchain in healthcare does one job – but in a pixel-perfect manner. It keeps patient data secure.
Adding new block (data) to blockchain-based EMR: This is how 100% accuracy is achieved using blockchain in healthcare
Each block contains the block number, nonce, patient data, hash, and the hash of the previous block.
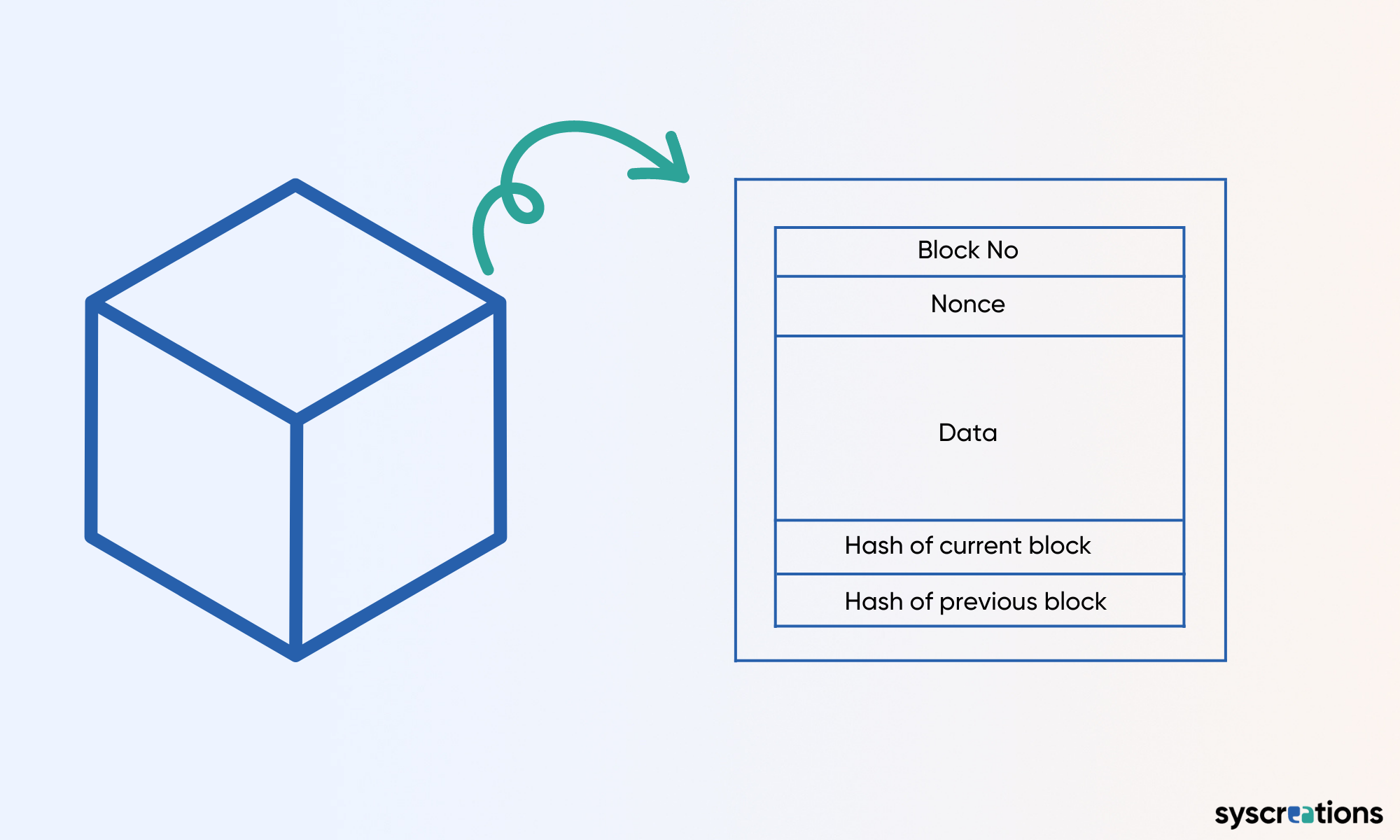
Nonce plays a very important role here. It is the number used to generate a hash value for that particular block.
For adding a new block to the blockchain network, it is important to generate a block’s hash value falling under a certain zone of hash values.
So, by changing nonce, we can generate the hash value that falls under our desired zone of hash values from the universe of hash values.
This desired zone of a hash value for a new block is defined based on the hash value of its previous block.
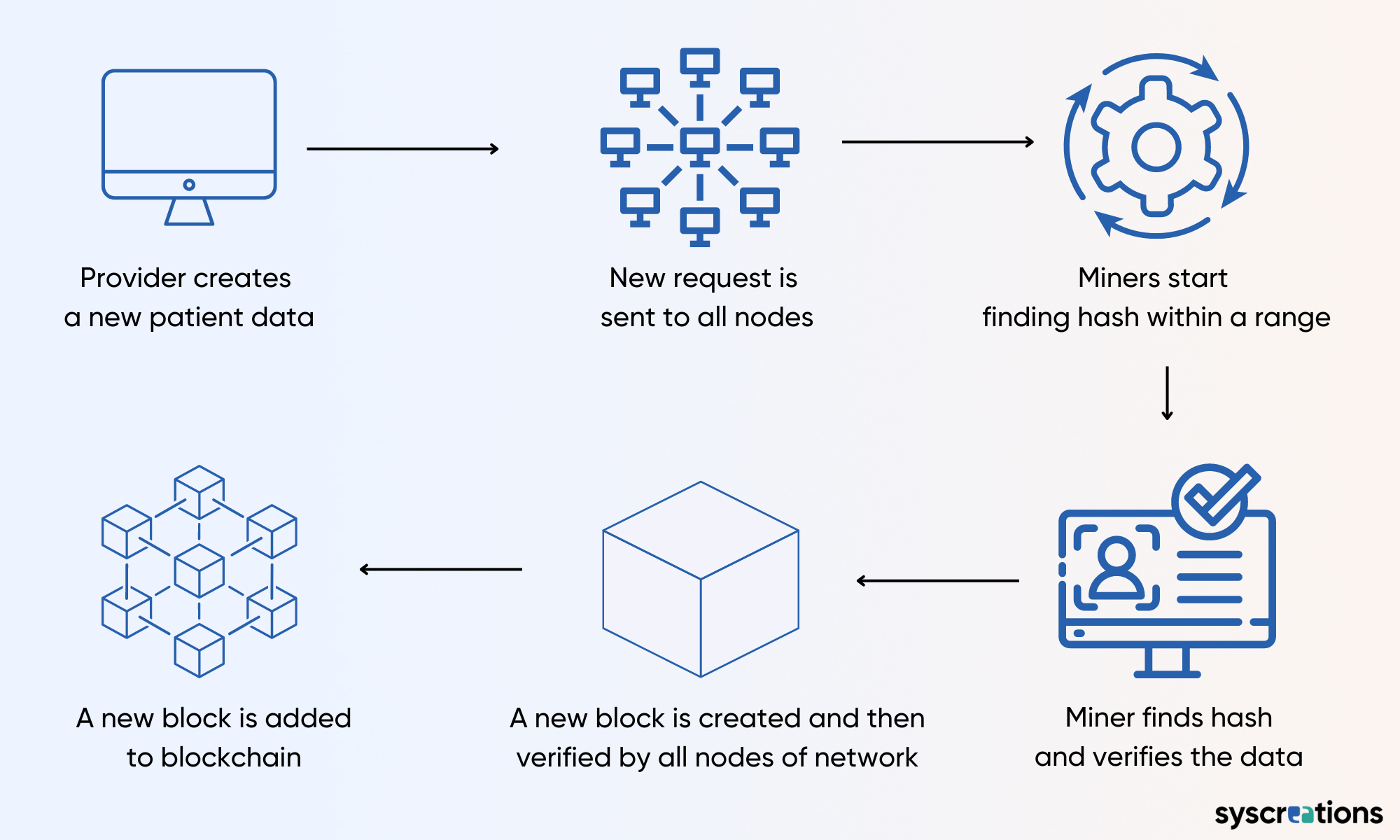
There are authorized stakeholders who keep changing the nonce to generate a hash value for a block.
This process is called mining which requires great computational power.
The mind-blowing part starts from here:
When a stakeholder finally finds the hash value for a block, he/she approves the block.
However, the block still cannot be added to the blockchain network.
In order to add it to the blockchain network, the block is now broadcasted to all nodes or stakeholders who verify the block and agree before adding that block finally to the blockchain network.
Stakeholders responsible for adding blocks are called miners and are also responsible for verifying the information, digital signatures, messages, and public keys of each block.
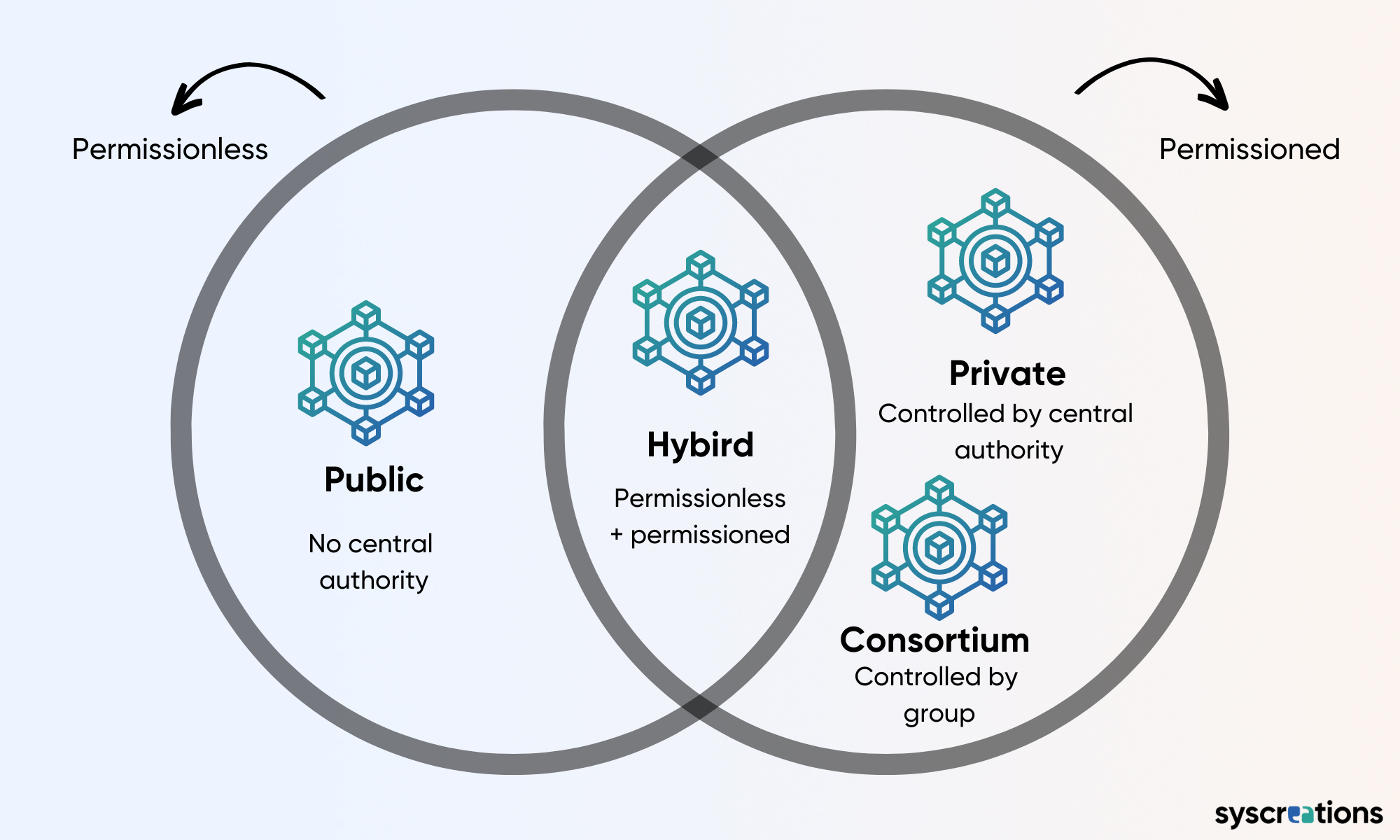
How to implement a blockchain-based EMR or blockchain in healthcare?
Blockchain offers a lot of flexibility when it comes to its implementation.
There are major four types of blockchain networks which you can select as per your target market, audience and business needs.
Conclusion – we asked our five random team members about similarities between them & blockchain
In case you don’t know yet, we are an Ontario-based healthcare-focused IT company.
We only practice healthcare IT projects as that’s the only way we found to bring project innovation – rather than just project delivery!
Anyway, here is how our team members responded to the question –
What are the similarities between you and blockchain?
- Lead UI/UX engineer (working remotely): “We both can neither be touched nor hacked!”
- Senior backend developer: “Big challenges no longer give both of us butterflies in the stomach!”
- Business analyst: “Users don’t see what we both see!”
- Compliance specialist: “People only think of us when they are trapped!”
- Sales manager: “You might hate us. But cannot ignore us!”