Today, healthcare facilities are swamped with health systems, databases, applications, processes, and devices.
They were to assist hospital staff and make care more patient-centric.
The concept failed.
As these systems were not interconnected, they became a maze of data for professionals.
EHRs, EMRs, Payer portals, Patient portals, and health systems have a huge gap between them.
Due to this, interoperability is in the spotlight.
If your systems are not working together, it becomes tedious for your staff to handle the tasks amidst the patient rush.
The Concept of Interoperability in the Healthcare Industry
Understanding your organization’s workflow will help you understand healthcare interoperability’s meaning.
You have Hospital Management Software on one side, Electronic Health Records on the other, and a discrete claims and billing management system.
According to a survey by Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society in 2021, 75% of healthcare providers report that their organization uses multiple EHR systems.
These systems become a single integrated unit when they become interoperable.
The health data flows seamlessly between the systems and easily establishes communication.
Interoperability in healthcare builds a unified environment for health data.
It can be set up on different levels depending on the care you wish to provide.
The goal of interoperability is to improve patient safety and operational efficiency, along with enhanced patient outcomes and health management.
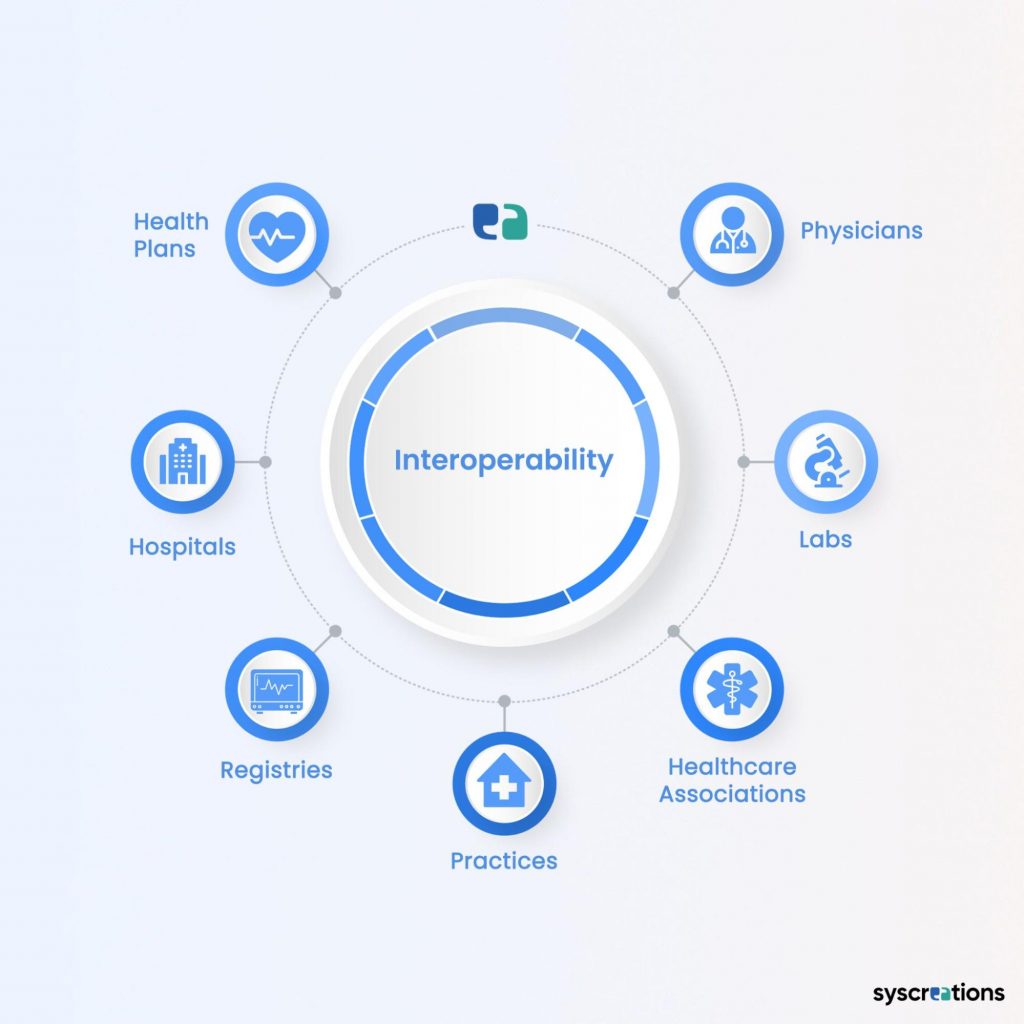
The Contribution of Interoperability in Healthcare
Interoperability in Healthcare facilitates integration and connections across different systems.
This information exchange should occur regardless of the applications, data origin, and target user, this information exchange should occur.
It ensures that the data is easily available.
Interoperability is a key element for decision support systems.
In healthcare, interoperability is achieved by using data exchange standards that allow data to be shared with hospitals, labs, pharmacies, patients, and clinicians regardless of application vendor.
Let us understand interoperability with an example.
If a patient has undergone a procedure in a hospital, the health information is recorded in the hospital computer system.
When the patient goes to the doctor’s office, he/she is not using the hospital computer.
With the use of interoperability, the provider will have the patient’s information and can easily do further treatment.
In What Ways Does Interoperability Confer Advantages to Healthcare Providers and Patients?
Implementing interoperability in healthcare facilitates enhanced patient care by granting providers access to comprehensive medical information.
This, in turn, enables providers to make well-informed decisions, thereby avoiding unwarranted tests and procedures.
Consequently, patients and providers can benefit from efficient medical data sharing.
Patients can easily access their medical records and possess control over their health information.
Providers can get all the medical information with less effort and time.
They can hassle-free share health information related to diagnosis, medications, and treatment with other providers.
Care coordination becomes easy.
As patient information is protected and managed securely, it helps with HIPAA compliance and security regulations.
Electronic health information can be shared seamlessly without any special effort by the users.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just someone looking to streamline their workflow, understanding the different types of interoperability can make your work a whole lot easier.
So, get ready to become an interoperability expert as we explore the five types in this blog.
From foundational to process interoperability, we’ve got you covered!
Types of Interoperability in Healthcare
Reaching the organizational and semantic level of interoperability is difficult, but it assures excellent results in the long run.
Benefits of Interoperability in Healthcare
Interoperability offers numerous benefits for healthcare professionals, including departmental heads and nurses, such as:
For Departmental Heads, interoperability provides more benefits:
- Improved data analytics
- Better resource planning
- Efficient use of staff time and resources
- Better reporting capabilities
For Nurses, interoperability can make their work easier by:
- Reducing administrative tasks
- Faster and more accurate documentation
- Improve communication with healthcare providers
- Reduce stress & burnout
- Better retention rates
- Improved job satisfaction
Interoperability can make the healthcare process patient-centric and hassle-free.
Exchanging information becomes easy and coordinated care is provided to the patient.
Interoperability must follow certain standards for managing and exchanging healthcare information with healthcare professionals and organizations.
Interoperability Standards for Managing and Exchanging Information
There are different health data standards for different healthcare needs.
Some standards are transmission, structure, code meanings, format, and data security.
Payers and clinical systems use different standards of data sharing.
The system must sanitize and manipulate data before importing it into another system.
In the US, all organizations must follow the following standards for the nationwide sharing of healthcare data.
Exchange healthcare information without the fear of HIPAA breach with an Interoperability facility.
Let us help you reach providers and staff of other departments with ease.
Are You Looking for a Way to Simplify Data Transfer Without Breaching HIPAA Compliance?
Interoperability has been in the industry for quite some time and is here to stay.
Regardless of the size of the practice, state and federal regulations apply to all.
It plays a massive role in making healthcare patient-centric and seamless data transfer between providers and patients from the healthcare computer system.
If you want to make the healthcare process smooth and provide better care to the patient, connect with us today to discuss your requirements and how we can help you achieve them.