Efficient supply chain management is essential to ensure the seamless flow of pharmaceutical products.
The pharmacy sector relies heavily on well-defined strategies to meet the demands of patients and healthcare providers.
There are many strategies in pharmacy supply chain management but, the most famous is the push and pull strategy.
What are the Push and Pull Strategies in Pharmacy Supply Chain Management?
Pharmacy supply chain management involves a complex web of activities, including
- Procurement
- Inventory management
- Distribution
- Delivery
Push and pull strategies are two prominent strategies used to streamline this process.
Let us delve into each one of these to understand it better.
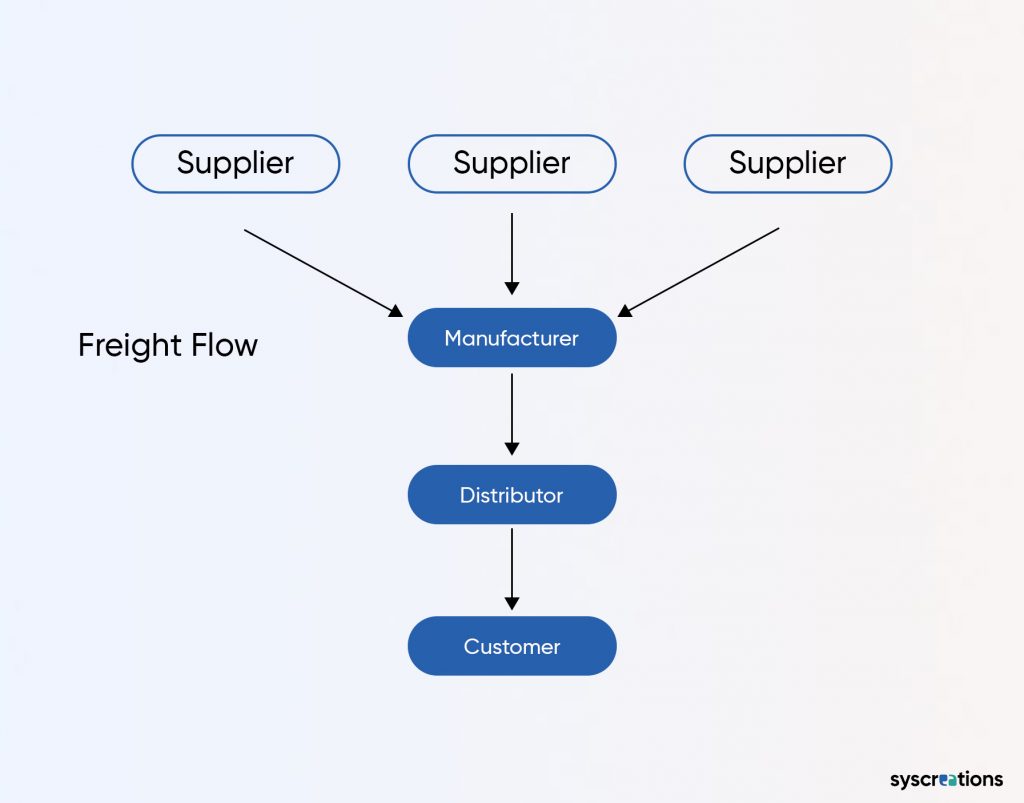
Push Strategy in Pharmacy Supply Chain Management
Pharmaceutical products are manufactured or procured in anticipation of demand.
Inventory levels are based on
- Historical data
- Forecasts
- Expected market trends
The push approach relies on proactive decision-making to ensure products are readily available when needed.
This method aims to minimize stockouts and delays in fulfilling orders.
The Advantage of the Push Strategy
The Limitations of the Push Strategy
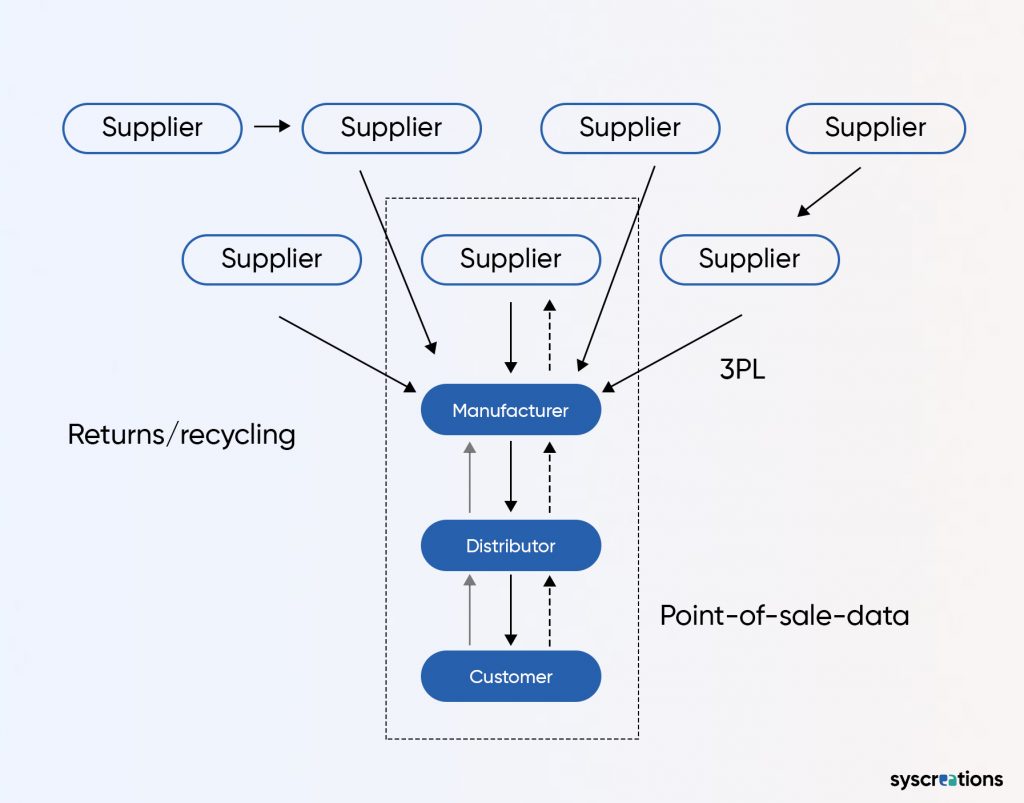
Pull Strategy in Pharmacy Supply Chain Management
Opposite to the push strategy, the pull strategy emphasizes a demand-driven approach.
Products are manufactured or procured based on actual customer demand.
This method ensures a lean inventory system, reducing the risk of excess stock and obsolescence.
The Advantage of the Pull Strategy
The Limitation of the Pull Strategy
The Role of Automation in the Pharmacy Supply Chain Management
Automation has emerged as a game-changer in pharmacy supply chain management.
By leveraging technological advancements, automation offers several benefits that can overcome the limitations of both push and pull strategies.
Unlock the Potential of Automation in Pharmacy Supply Chain Management
Pharmacy supply chain management is a complex endeavor that requires careful consideration of strategies and technologies to ensure timely access to vital pharmaceutical products.
Both push and pull strategies have their advantages and limitations.
But automation emerges as a powerful tool to overcome these challenges.
By using automation in pharmacy supply chain management, pharmacies can ensure seamless access to medications and better healthcare outcomes for patients.
With over 8 years of experience in the healthcare software development industry, we, at SyS Creations, have established ourselves as a leading provider of pharmacy software solutions.
The user-friendly interface and intuitive design of our solutions make it easy for pharmacists and staff to navigate and utilize the software effectively.
We can help you explore our pharmacy automation software solution, which encompasses these strategies and more, to transform your pharmacy supply chain management processes.



